Liver Disease and diet – A guide for adult patients, their carers and families
What is Liver Disease ?
There are many different types of liver disease. You can help prevent or reverse some of them by maintaining a healthy weight and staying within the recommended alcohol limits if you drink. Some types are :
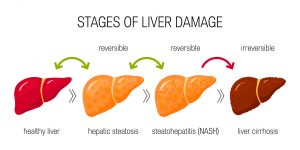
- Alcohol-related liver disease caused by regularly drinking too much alcohol. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (steatohepatitis -NASH) caused by obesity leading to fatty deposits within the liver.
- Hepatitis caused by a viral infection and sometimes related to excessive alcohol consumption.
- Haemochromatosis caused by a genetic abnormality.
- Primary biliary cirrhosis often caused by a problem with the immune system.
What are the symptoms of liver disease?
Most types of liver disease do not cause any symptoms in the early stages. Once you start to get symptoms of liver disease, your liver is already damaged and scarred. This is known as cirrhosis and cannot be reversed.
The common symptoms are :
- feeling very tired and weak all the time
- loss of appetite – which may lead to weight loss
- loss of sex drive (libido)
- yellow skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- itchy skin, or feeling or being sick.
Treatment for Liver disease
The goal of treatment is to slow down the build
-up of scar tissue and prevent or treat any problems that arise. This can be achieved through a healthy diet and lifestyle. When you are unwell with liver disease, your body has a higher demand for energy and protein. This is because the liver plays a major role in storing and releasing energy and protein, and when it is not working well these functions do not work properly either. Good nutrition can help overcome symptoms of liver disease and prevent complications by:
- Slowing down muscle wasting
- Helping wounds heal more quickly
- Helping prevent and fight infections
Eat little and often and the importance of Starchy Foods
Instead of having three main meals aim to eat something every 2 to 3 hours and eat a snack before bedtime. This should be something high in starchy carbohydrates such as cereal, porridge, rice pudding or shortbread. It is important to have regular meals and snacks which contain starchy carbohydrate, ideally every 2-3 hours during the day. Starchy carbohydrate containing foods include bread; potato; cereals & cereal bars; pasta; noodles; rice; and biscuits or crackers.
Carbohydrate bedtime snack
It is important to have a bedtime snack containing 50g of carbohydrate as it is a long time until breakfast.